If 1995 seems a long time ago, that’s because it was. The DVD player was the hot new entertainment device, mobile phones were bulky and did little besides place calls, and accessing the internet was a novel (and slow) experience confined to desktop computers.
Technology has changed immensely in the 25 years since then. One could argue that it’s continued to improve our lives, keeping us more connected to information, entertainment and each other. You also could argue just the opposite, but either way, there are a few gadgets and technologies that have changed our lives and the world forever.
This is the third in a five-part series on technologies that have impacted the world.
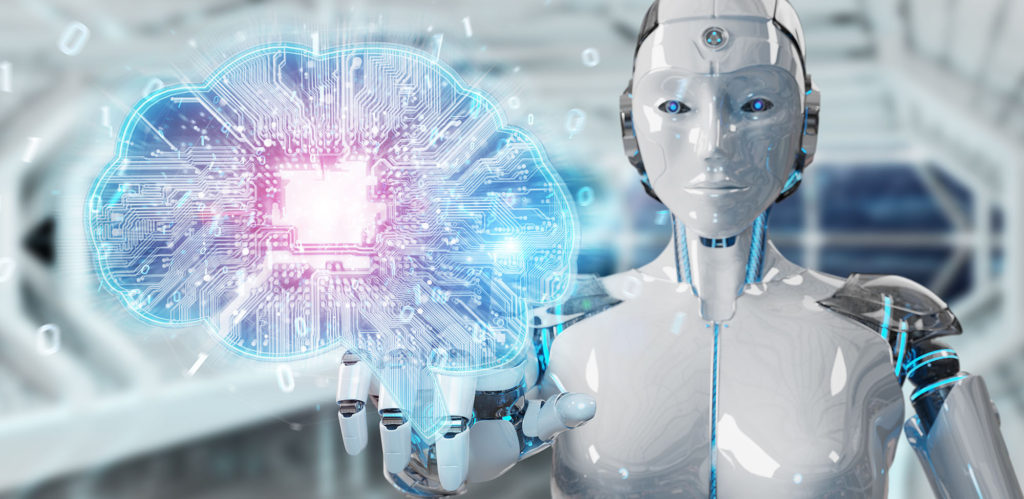
Artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence – simulating human intelligence in machines – used to be confined to science fiction. But in recent decades, it’s broken into the real world, becoming one of the most important technologies of our time. In addition to being the brains behind facial recognition, AI is helping to solve critical problems in transportation, retail and health care (spotting breast cancer missed by human eyes, for example). On the internet, it’s used for everything from speech recognition to spam filtering. Warner Bros. even plans to use AI to analyze its potential movies and choose which ones to put into development.
But there’s also fear that a dystopian future is looming with the creation of autonomous weapons, including drones, missile defense systems and sentry robots. Industry leaders have called for regulation of the technology to prevent the potential harm from tools like deepfakes, which are video forgeries that make people seem to say or do things they didn’t.
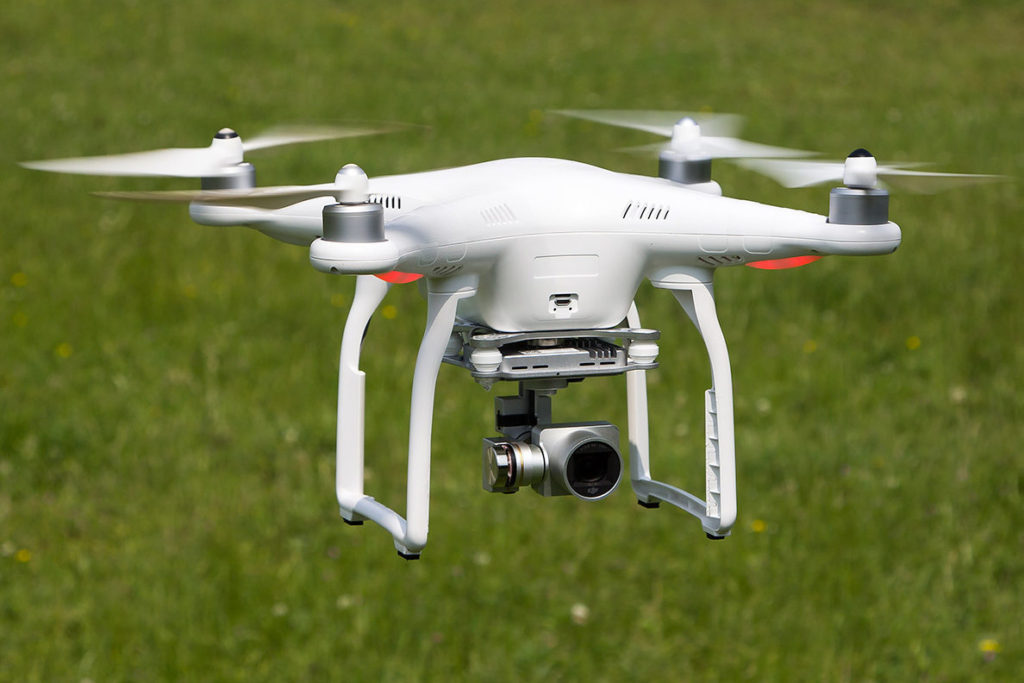
Drones
Drones have really taken off in recent years. What started out as a hobbyist gadget has transformed industries, with the unmanned aircraft shooting movie sequences, delivering packages to hard-to-reach places, surveying construction sites and spraying pesticide over crops to protect farms.
Drones now range from noisy quadcopters to payload-carrying mini-planes. On the US-Mexico border, Customs and Border Protection uses $16 million military-style Predator drones that can fly as high as nine miles, equipped with radar strong enough to detect footprints in the sand.
In the not-too-distant future, drones are expected to crowd the skies, acting as personal air taxis and performing lifesaving duties such as delivering medicine, helping with search and rescue, and fighting fires.
DNA testing kits
With a simple swab of your cheek or a sample of your saliva, DNA testing kits have helped deepen our understanding of ancestry, introduced us to living relatives around the world, determined paternity and shed light on a predisposition to specific health issues and diseases.
Over the past few years, the kits have become quite affordable and popular. Law enforcement agencies in particular have grown fond of the kits. Using a technique called genetic genealogy, they’ve cracked dozens of murder, rape and assault cases, some from decades ago.
Then investigators use traditional genealogical research to identify possible suspects, who are then tested for a DNA match to the crime scene. But the practice relies on investigators having access to a large cache of DNA profiles, and it stirs worries among privacy watchdogs.
Quantum computing
Companies and countries are pouring billions of dollars into quantum computing research and development. They’re betting it will pay off by opening up new abilities in chemistry, shipping, materials design, finance, artificial intelligence and more.
The technology is beginning to show some of the promise researchers have hyped for decades. Last year, a Google-designed quantum processor called Sycamore completed a task in 200 seconds that, by Google’s estimate, would take 10,000 years on the world’s fastest supercomputer.
Honeywell, which once sold massive mainframes, predicts the performance of its quantum computers will grow by a factor of 10 every year for each of the next five years — meaning they’d be 100,000 times faster in 2025.
Social networking
The online world was a very different place two decades ago. Social networkers of a certain age may remember Friendster, the site that launched in 2002 and allowed people to fill out an online profile and connect with people they knew in real life. But two years later, Mark Zuckerberg changed everything when he launched a social-networking site for college students called Facebook. It opened to the general public in 2006 and quickly left Friendster and MySpace far behind.
Today Facebook helps people connect and stay connected, but its real business is advertising. Last year, it brought in $32 billion in ad revenue. It also helped pave the way for other social networks that help people chat, share photos and find jobs, among other activities. It now has 2.37 billion users – nearly a third of the world’s population.
Source: cnet.com/ Author: Steven Musil
Send your news, stories or articles to info@chrife.com.gh or via Whatsapp +2332550144803